

What Is Web 3.0 And How Does It Affect The Future?
16 March 2022
For the last two decades, the Internet has been around. It has been the bedrock of our life and development. Currently, millions of people utilize it every day, generating value for our economy and propelling human civilization forward. We are now in the process of transitioning to a decentralized network, dubbed Web 3.0.
While this may seem to be an insurmountable condition, it has already begun to deteriorate. So, without further ado, let bePAY get down to the complete definition of Web 3.0 and its ecosystem.
What Is Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 Definition
Web 3.0 is the next generation of the Internet. As disruptive and paradigm-shifting as Web 2.0, Web 3.0 symbolizes the next step in the development of the web and the Internet. There are three pillars of Web 3.0: decentralization, transparency, and increased value for the user.
In the 1990s, Berners-Lee explained some of these notions, as detailed below:
- No central authority is required to put anything on the web, there really is no central controlling node, and hence no single point of failure…and no ‘death switch! ‘” Freedom from censorship and snooping is an important part of this.
- Code was not authored and managed by a limited number of professionals, but rather evolved in plain view of everyone, promoting maximum engagement and experimentation.

Web 3.0 definition
When discussing the Semantic Web in 2001, Berners-Lee referred to it as a “Semantic Web.” Semantic processing is beyond the capabilities of computers. His idea for Semantic Web was to organize web material and make it possible for software that could do complex tasks for users to be developed.
Web 3.0 has gone far beyond Berners-initial Lee’s vision of the Semantic Web in 2001. A combination of the difficulty and expense of translating human language, with all of its complexity and diversity, into an electronic format that computers can easily understand, as well as the fact that Web 2.0 has grown significantly over the last two decades, is to blame.
>> Read also: What is GameFi and why GameFi is crypto’s hot new thing?
Go Back To The Past
Before we dig farther into web 3.0, we really have to comprehend how we got here — through web 1.0 and web 2.0. An overview of the Internet’s history may be found here:
- Web 1.0 is a read-only web where individuals may read the information posted on websites.
- Web 2.0 is a read-write web where individuals may read and produce information on websites and apps.
- Web 3.0 is a read-write-interact web (driven by artificial intelligence) where individuals may read, create and interact with the material, including 3D visuals, on websites and applications.
Let’s take a closer look at each stage of the Internet’s development.
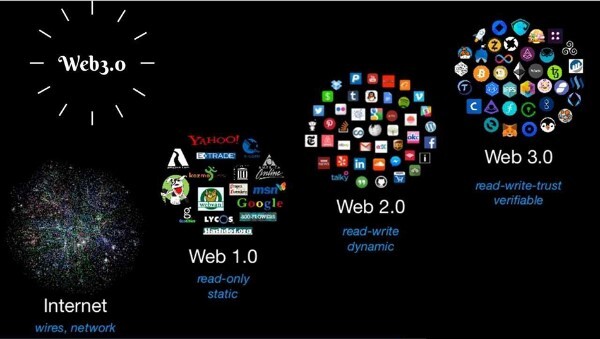
The new age of web 3.0
Web 1.0 (1989-2005)
Web 1.0 debuted in 1989 and was active until 2005. Sir Tim Berners-Lee founded the World Wide Web in 1989 while working at CERN. The key components of the first version of the web:
URL (Uniform Resource Locator)
HTML (HyperText Markup Language)
HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol)
The fundamental goal of web 1.0 was to locate information. Significantly, web users could not participate freely since it was “read-only,” therefore any dialogue was done offline.
Moreover, as there were no search engines accessible during this iteration, surfing the World Wide Web (WWW) was not nearly as straightforward as it is today. To access any website, you need the URL to be memorized. The Internet used to “browse” by “going through FTP file directories screen by screen and hoping that the file we sought was in there someplace,” as one tech journalist remembers from the past.

Web 1.0
However, during the mid-1990s, Netscape Navigator emerged as the first web browser, and developed key browser features we still use today:
- Presenting a web page as it loads
- The creation of forms and interactive content
- Using Javascript and the storage of session data through cookies,
Unfortunately, during the so-called browser wars, Microsoft completely destroyed Netscape.
The Next-Generation Web 2.0 (1999-2012)
Darcy DiNucci initially invented the phrase “web 2.0” in 1999 in her paper “Fragmented Future”. However, it was subsequently popularized by Tim O’Reilly and Dale Dougherty in late 2004.
At this point in the web’s evolution, the majority of us feel comfortable using it. By 1999, individuals were beginning to be able to connect with one other on the Internet through social networking platforms, content blogs, and other services. Eventually, smartphones were built and mobile computing was introduced.
People started communicating online in discussion forums and generating material that other Internet users could access and enjoy, comment on or share. Instagram influencers, Yelp reviews, and other forms of social proof have become ubiquitous in recent years. The read-only mode became outmoded, and web 2.0 was now pushed as a platform for interaction.

Web 2.0
Web 2.0, as described by O’Reilly and others between 1999 and 2004, changed the globe away from static desktop web pages built for information consumption through pricey servers and toward interactive interactions and user-generated content.
Web 2.0 gave rise to companies like Uber, Airbnb, and Facebook, among others. Web 2.0 Core Layers of Innovation. The advent of web 2.0 was driven largely by three major levels of innovation:
- Mobile
- Social Media
- Cloud
Why Web 3.0?
Toward the end of 2012, Web 2.0 began to fade away, and people began to become aware of Web 3.0. Google, Facebook, Microsoft, and Amazon’s dominance in current services has sparked a few objections. Large enterprises and small businesses alike have been accused of snooping on their customers’ personal information because of the lack of control they were given over their data use.
Businesses are accused of treating customers unjustly, abusing their personal information, and endangering free expression and democracy. Amazon’s aggressive commercial methods, Facebook’s privacy breaches, and Google’s data privacy difficulties and unethical AI usage all raise major safety alarms regarding web 2.0, according to a number of recent publications.
Because of this, many blockchain experts believe that web 3.0 is a more secure version of the internet.

Web 3.0 revolution
Web 3.0 (2006-ongoing)
“Web 3.0” came into being in 2006 when New York Times reporter John Markoff coined this term: “In many respects, web 3.0 is a return to Berners-original Lee’s Semantic Web concept,” he wrote. Web 3.0’s Layers:
As opposed to the mobile, social, and cloud technologies that propelled Web 2.0, three additional layers of technical innovation fuel Web 3.0:
- Cut-edge computing
- Decentralization
- Machine learning and AI
- Blockchain technology
What Are Examples Of Web 3.0 Applications?
Web 3.0 dApps have already begun the transformation. There are a number of distinct dApps that will eventually replace conventional services and apps, therefore we’ll break them down into categories. It is possible to develop decentralized organizations’ business models using dApps. It’s just a matter of time until these applications are adopted by the masses. You need to know a lot about decentralized applications (dApps) to have a good grasp of Web 3.0.
You can easily keep track of the many categories by looking at the list provided below. Listed below are the details.
- Exchange Services
- Social Networks
- Messaging
- Streaming (Video and Music)
- Remote Job
- Storage
- Insurance and Banking
- Browser

Web 3.0 exapmles
But to those who are cryptocurrency traders/investors what does the web, 3 2022 mean to them?. If they believe in blockchain technology and web 3.0 futures, investing in the top coin web 3.0 is a good idea let’s move to the names of coin web 3 2022 you can take into consideration
What Is The List Of Coin Web 3.0?
Polkadot (DOT)
Polkadot is among the world’s most popular cryptocurrencies, yet many investors are unaware that it is a Web 3.0 initiative. The network is well-known for its scalability, and when compared to Ether, it scores better in terms of cheap costs and quick speeds. Due to its market dominance and progressive increase in market value, DOT may claim to be the dominant player and the decentralized internet industry’s leader.
Helium (HNT)
Helium is a decentralized blockchain-based network for IoT devices that makes use of a worldwide network of low-energy wireless hotspots to broadcast data to the blockchain through radio waves. The network validates that hotspots are delivering real wireless service using a novel technique called proof-of-coverage consensus.

Helium
BitTorrent Protocol (BTT)
BitTorrent is the world’s largest first torrent tracker and the world’s most powerful peer-to-peer system. Large files are fragmented and delivered over the web in fragmented form, where they are merged into a single file on the recipient’s computer. Each user who downloads a file from the network becomes an immediate member of the distribution.
Oceans Protocol (OCEAN)
OCEAN is another cryptocurrency that provides all of the necessary tools for developing a Web 3.0 solution. The coin is one of the greatest options for individuals seeking a Web 3.0 token with significant upside potential. The protocol has produced a number of tools required for Web 3.0 application development.
Additionally, the protocol focuses on decentralizing the notion of data sharing on the internet, which enables access and transparency in the data management process.
Storj
A major decentralized storage option is Storj. Additionally, it’s a relic from antiquity. Anyone may store data using Storj. It’s free and simple to use, too. 1-Click Start makes it easy for anybody to get started. Because consumers may pay as they go, the business is built around them. The Storj token is used to run the Storj platform.

Storj
Sia
As with Storj, Sia is a promising decentralized storage system with the potential to be Storj’s largest rival. A 30-segment chunk of the file is then sent to each of the thirty recipients. During the transmission, the file is encrypted as well.
Filecoin
Filecoin is the final project we’d like to mention. Protocol Labs is working on this project, which takes a dual approach and makes use of two different kinds of network nodes.
>> Learn more: What is burning crypto? Who does it benefit?
FAQs About Web 3.0
Does Web 3.0 Already Exist?
Does Web 3.0 Already Exist? – Due to the fact that Web 3.0 has not yet been deployed, there is no definitive definition. It took over a decade to shift from Web 1.0 to Web 2.0, and it is predicted to take at least as long, if not longer, to completely deploy and transform the web with Web 3.0.
However, others feel that the technologies that will comprise and eventually define Web 3.0 are now being created. The use of wireless networks in smart home appliances and the Internet of Things (IoT) are two examples of how Web 3.0 is already influencing technology.

Does web 3.0 already exist?
But to those who are cryptocurrency traders/investors what does the web, 3 2022 mean to them? If they believe in blockchain technology and web 3.0 futures, investing in the top coin web 3.0 is a good idea let’s move to the names of coin web 3 2022 you can take into consideration
Which Newer Financial Technologies Will Be Helped Facilitate By Web 3.0?
Due to the fact that Web 3.0 is fundamentally decentralized, it fits itself to technologies like blockchain, distributed ledger, and DeFi.
What Are The Real Examples Of How Web 3.0 Will Increase User Utility?
For instance, if you’re planning a trip and are on a budget, you’d now have to spend hours browsing through different websites and comparing pricing. Web 3.0 will enable intelligent search engines or bots to aggregate all of this data and create personalized suggestions based on your profile and interests, saving you hours of searching.
Closing Thoughts
To summarize, Web 3.0 will make the internet a more equal place for everyone by empowering each user to be their own sovereign. To be really sovereign, one must be able to own and control who benefits from their time and knowledge.
Web 3.0’s decentralized blockchain technology will allow individuals to connect to a web where they may own and be fairly rewarded for their time and information, eclipse an oppressive and unfair web, where huge, centralized archives are the only ones that own and benefit from it.
To draw an example from the movies, if Web 1.0 represented the black-and-white movie period, Web 2.0 would be the age of color/basic 3D, while Web 3.0 would be immersive experiences in the metaverse. While Web 2.0 dominated worldwide business and culture in the 2010s, it’s possible that Web 3.0 may accomplish the same thing in the 2020s.
Facebook changed its name to Meta on Oct. 28, 2021, which might well turn out to be an early warning that the move to Web 3.0 is getting up momentum. To learn more about other blockchain technology and cryptocurrency posts, click here.

What Are Stablecoins And Why Do You Need Them?
10 March 2022
What Is Taproot Bitcoin? How Does It Affect Bitcoin?
24 June 2022










