

Blockchain Technology Goes Beyond The Use Of Cryptocurrency
29 March 2022
Most likely in the last few years, you’ve come across discussions about blockchain technology vs cryptocurrency a lot. These two concepts are expected to change the way we think about information technology and banking.
Many people confuse the phrase blockchain technology vs cryptocurrency which are two different things. There is, however, a critical contrast between the two. The blockchain is a public ledger used to record cryptographic transactions, making cryptocurrencies a kind of digital currency. Aside from storing and retrieving cryptocurrency, blockchains may store and retrieve medical data, logistics chain data, and financial information.
An asset’s origin may be recorded in a decentralized, distributed ledger known as the blockchain. By its very nature, a blockchain’s data can’t be changed, which makes it a genuine disruptor in fields such as payments, cybersecurity, and health care. As a result of this bePAY tutorial, you now have a better understanding of exactly what is blockchain technology, blockchain application, and why it is so crucial.
What Is Blockchain Technology?
Transactions and assets in a business network may be recorded and tracked in an immutable ledger called the Blockchain. There are two types of assets: tangible and intangible (intellectual property, patents, copyrights, branding). A blockchain network may be used to monitor and exchange almost anything of value, decreasing risk and lowering costs for everyone involved.
The reason blockchain is so crucial: Information is the lifeblood of business. The better it is, the quicker it is received and the more precise it is. That information can be sent quickly, securely, and entirely transparently via the use of blockchain technology, which can only be viewed by network users who have been granted permission.
Orders, payments, accounts, production, and more may all be tracked on a blockchain network. Because everyone has access to the same understanding of reality, you can see all the intricacies of a transaction from beginning to finish, providing you more confidence and allowing you to take advantage of new possibilities.

Blockchain technology
Blockchain’s most important components:
- Distributed ledger technology: Transactions are recorded in the distributed ledger, which is accessible to all network members. A conventional corporate network’s duplication of effort is eliminated by using a single shared ledger to record all transactions.
- Immutable records: After a transaction has been logged to the shared ledger, no one can alter or tamper with it. If a mistake is found in a transaction record, a new transaction must be created to correct the problem.
- Smart contract: A set of rules known as a “smart contract” is recorded on the blockchain and is automatically performed to accelerate transactions. A smart contract may set criteria for corporate bond transfers, provide rules for travel insurance to be paid, and more.
How Does Blockchain Work?
To understand how blockchain technology works, we must first understand what it is. You may have noticed a recent uptick in the number of companies using blockchain technology. However, how does blockchain technology operate exactly? Is this a major addition or a little tweak? To begin demystifying Blockchain, let’s take a look at some of the most recent developments in the technology.
There are three prominent technologies in the blockchain: Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin.
- Keys used in cryptography
- A data storage system for network transactions and records
- A data storage system for transactions and records
Cryptographic keys are classified as private or public. Using these keys, transactions between two parties may be completed successfully. These are the two keys that each person has and uses to create a private digital identity. The most significant component of blockchain technology is the ability to safeguard an individual’s identity. This identification is known as a “digital signature” in the bitcoin world, and it is used to authorize and manage transactions.

How does blockchain work?
In the peer-to-peer network, a large number of people who operate as authorities utilize the digital signature to agree on transactions and other problems in general. When they approve a trade, a mathematical verification certifies it, resulting in a successful secured transaction between the two network-connected parties. To summarize, the peer-to-peer network of blockchain users uses cryptographic keys to accomplish many forms of digital exchanges.
>> Read also: What is multichain technology? Compare multichain vs cross chain in crypto
Types Of Blockchain
Each sort of blockchain has its unique characteristics. Listed above are their names, according to the sources:
Private Blockchain Networks
It is common for private enterprises and organizations to benefit from private blockchains, which run on private networks. A company’s access and permission preferences, network specifications, and other critical security choices may all be tailored using private blockchains. A private blockchain network can only be managed by a single authority.
Public Blockchain Networks
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) was popularized by public blockchains, which were the genesis of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. As an added benefit, public blockchains reduce the risk of security problems and centralization.
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) uses a peer-to-peer network to store data rather than a single site. Consensus algorithms are often used to validate data validity, such as Proof of Stake (PoS) or Proof of Work (PoW).
Permissioned Blockchain Networks
Permissioned blockchain networks, also known as hybrid blockchains, are private blockchains that only allow access to approved parties. There are several advantages to using these sorts of blockchains for business purposes, such as improved control over who may join the network as well as which transactions are allowed.

How many types of blockchain?
Consortium Blockchains
Permissioned blockchains include both public and private components; consortium blockchains, on the other hand, contain both public and private components, but only one consortium blockchain network will be managed by many companies.
The setup of these blockchains might be more difficult, but once they are up and running, they can provide higher security than other kinds of blockchains. Consortium blockchains are the best choice for multi-organizational cooperation because of their scalability.
Blockchain Technology Advantages
We have gone through the definition of blockchain technology and its types of them. Now, let’s discuss its advantages.
More Reliable Transactions
The fact that many nodes must verify a blockchain transaction helps to limit the possibility of a mistake. The other nodes would notice something is amiss and correct it if a mistake was made in the database on one of them. In a conventional database, on the other hand, an error is more likely to be accepted. In addition, each asset is recognized and monitored on the blockchain ledger, preventing duplicate spending.
Middlemen Are Not Necessary
It is possible to accomplish a transaction between two parties without the involvement of a third party using blockchain technology. You don’t have to pay a middleman like a bank for this, which saves time and money.
There is a tremendous deal of potential in blockchain technology, which may bring more efficiency to all digital commerce, to promote financial empowerment to the unbanked or underbanked people of the globe.

Benefits of blockchain
Added Protection
It is theoretically difficult for someone to commit fraud on a decentralized network, such as a blockchain. Every node and every ledger would have to be hacked and changed to put in bogus transactions. It is not impossible, but adding fraudulent transactions is difficult and not in the interest of participants in many cryptocurrency blockchain systems that utilize Proof of Stake or Proof of Work transaction verification mechanisms.
Faster
People may move money and assets more quickly, particularly globally, since blockchains run around the clock. Rather than waiting for a bank or government agency to personally verify everything, they don’t have to.
Blockchain disadvantages: transactional capacity is limited to one per second.
There is a limit to how rapidly the blockchain can move since it relies on a wider network to approve transactions. There are just 4.6 transactions per second on Bitcoin, compared to 1,700 transactions per second on Visa. Increased transaction volume might also slow down the network. Scalability is a problem till this gets better.
Blockchain Application
From delivering financial services to managing voting systems, blockchain technology serves a wide range of functions.
Cryptocurrency
As a foundation for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, blockchain is widely used today. A blockchain is used to keep track of all transactions involving Bitcoin. Blockchain may become more widely used if more people started using cryptocurrencies.
Cryptocurrencies are still not widely utilized to pay for goods and services because of their high volatility. As noted by Foley & Lardner senior partner and leader of the firm’s blockchain task force, Patrick Daugherty, this is changing as PayPal, Square, and other money service organizations make digital asset services widely accessible to suppliers and retail consumers.

Blockchain application
Banking
Transactions in fiat money, such as dollars and euros, are also being processed using blockchain technology. Compared to transferring money via a bank or other financial institution, this method may be more efficient since transactions may be checked and executed outside of usual business hours.
Assets Transferring
It is possible to keep track of and transfer ownership of certain assets using the blockchain as well. With digital assets like NFTs, a digital representation of ownership of digital art and media, this is now quite popular.
There are many more uses for blockchain technology, such as transferring the ownership of the real estate and automobiles. The blockchain would be used by both parties to verify that one has ownership of the property and the other has the necessary funds to purchase it, and then the transaction could be completed and recorded.
Without having to submit documentation to the local county government, they could transfer the property deed and it would be instantly updated in the blockchain.
Smart Contracts
Another blockchain innovation is self-executing contracts, or “smart contracts.”. Once the prerequisites are satisfied, the digital contracts go into effect automatically. Payment for an item, for example, may be released immediately upon fulfillment of all transaction requirements by the buyer and seller.
The use of blockchain technology and written instructions to automate legal contracts is something Gray believes has significant promise. Outside third parties may be minimized or even eliminated in the case of a correctly written smart legal contract on a distributed ledger.
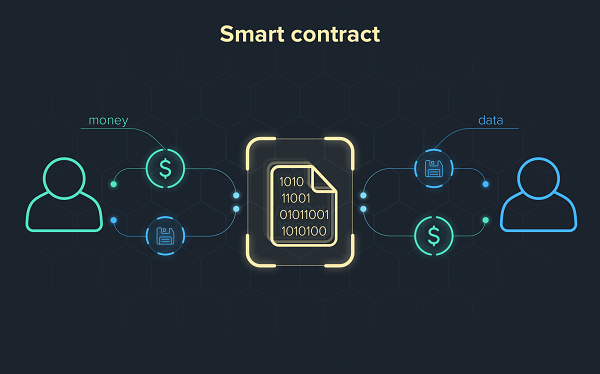
Smart contracts
Supply Chain Tracking
As items move from one region of the globe to the next, supply chains are flooded with data. It’s difficult to find out where a vendor’s low-quality items come from when using typical data storing techniques.
In the case of IBM’s Food Trust, which employs blockchain technology to track food from cultivation to consumption, storing this information on the blockchain would make it simpler to return and monitor the supply chain in the future.
Voting
Voting fraud is being investigated by experts in the field of blockchain technology. For blockchain voting, tamper-proof ballots and the elimination of the need to physically collect and validate paper ballots are theoretically possible.
Blockchain Technology Vs Cryptocurrency
Although many people think blockchain technology and cryptocurrency are one, there are big distances between them. Let’s discover what they are.
The Same Traits Of Blockchain Technology And Cryptocurrency
Below are some main traits that are the same:
- Nonphysical
Both the blockchain and the cryptocurrency are immaterial concepts. In contrast to the dollar, which you can grasp in your hand, cryptocurrency is an immaterial digital token. There is no one location or data centre where Bitcoins are stored on the blockchain.
- Advanced
Blockchain and cryptocurrency are both technical breakthroughs. Blockchain technology is the backbone of cryptocurrencies. Traditional databases, on the other hand, are much less modern and less safe. Cryptocurrencies are more sophisticated in terms of technology than traditional fiat currency.
- Interdependent
Bitcoin, the world’s first cryptocurrency, used an interdependent blockchain to keep track of its transactions. To keep track of all the transactions, the most popular cryptocurrencies use blockchains. A Bitcoin blockchain is created whenever a new Bitcoin is purchased.

Blockchain vs cryptocurrency
Blockchain And Cryptocurrency Disparities
The following are some significant distinctions between them:
- Nature
Data may be stored on a decentralized network using blockchain technology. In a similar vein to the US dollar, cryptocurrencies serve as a means of trade. In addition to holding Bitcoin transaction records, a blockchain may be used to store other forms of data.
- The value
There is a monetary value to all cryptocurrencies. But there is no monetary value to a blockchain.
- Usage
In addition to cryptocurrency, blockchain technology offers a wide range of other applications. Supply chain and retail companies may all benefit from the adoption of blockchain technology. It is a kind of digital currency that may be used to purchase products and services, as well as to invest.
- Mobility
Blockchain technology is decentralized and dispersed around the globe. A blockchain does not have a central repository where all of its records may be found. Mobile wallets may be used to access cryptocurrencies, even though they are stored on the blockchain. With a bitcoin wallet, you may transact with anybody who accepts digital currency anywhere.
- Transparency
As a public ledger, blockchain is very transparent. Access to blockchain network data is free for everyone who joins it. Cryptocurrencies, on the other hand, allow for complete secrecy. There is no way to determine who is behind a Bitcoin transaction, even though everybody can see the origin and destination of the transaction.
Some FAQs About Blockchain
What Is The Exact Number Of Existing Blockchains?
The number of active blockchains is rising every day at an ever-increasing speed. By 2022, there will be more than 10,000 blockchain-based cryptocurrencies in use, as well as several hundred non-crypto currency blockchains, according to the report.

Some FAQs about blockchain
What Is The Distinction Between Public And Private Blockchains?
A permissionless or open blockchain, often known as a public blockchain, allows anybody to join and run a node on the network. These open blockchains need encryption and a consensus technique like Proof of Work to be safeguarded because of their open nature (PoW).
A private or permissioned blockchain, on the other hand, needs each node to be vetted before joining. Because nodes are trusted, there is less need for as many levels of protection.
Who Developed Blockchain?
Blockchain technology was initially developed in 1991 by Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta, two scientists who aimed to design a system where document timestamps could not be manipulated with. In the late 1990s, cypherpunk Nick Szabo advocated utilizing a blockchain to secure a digital payments system, known as bit gold.
>> You may also like: Top best crypto books 2022 – The guide for beginners to cryptoworld
Wrapping Up
With numerous practical uses for the technology already being deployed and researched, blockchain is finally earning a reputation for itself in no little part due to Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies. As a term on the tongue of every investor in the country, blockchain aims to make corporate and government processes more precise, efficient, secure, and affordable, with fewer middlemen.
As we enter the third decade of blockchain, the issue is not whether but when will traditional organizations adopt the technology. Assets are being tokenized as well as NFTs proliferate. The following decades will show to be a significant time of development for blockchain.

What Are Stablecoins And Why Do You Need Them?
10 March 2022











