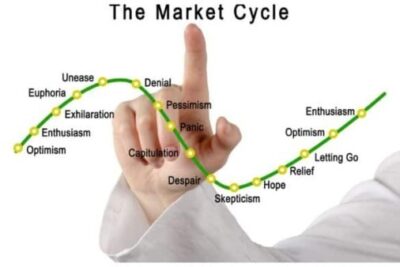
What Are Nodes – How Many Types Of Nodes Crypto In Blockchain Technology?
27 July 2022
The word “node” refers to any component that functions as a component of a larger network in the field of computer science. In the realm of cryptocurrency and blockchain, a node refers to one of the computers that are used to verify and preserve the whole history of transactions that have taken place throughout the network. The blockchain software is executed on these nodes.
In this post, bePAY will try to clarify what are nodes in the simplest way for you, as well as other information about nodes in the blockchain with the types of crypto nodes list. Do not wait any more, let’s jump into the definition of what are nodes.
What Are Nodes?
Blockchain nodes refer to a network’s stakeholders and/or their equipment, which are allocated to store a copy of the distributed ledger and act as communication hubs that carry out numerous crucial network operations? The primary function of a blockchain node is to validate the legitimacy of successive batches of network transactions, called blocks. Unique identification is linked to each node’s device, allowing it to be distinguished from other nodes in the network.
A proof-of-work (PoW) blockchain, such as Bitcoin (BTC) or Monero (XMR), includes miners with the following responsibilities:
However, only “full nodes” are needed to store all blockchain transactions locally. Validating blocks and transactions is within the purview of these nodes. On the other hand, lightweight or light nodes have reduced storage needs since they just need to download block headers to validate transactions. These variants of a complete node do not always include a block reward.

What are nodes in crypto explanation?
The availability of a blockchain node is another approach to categorizing it. An “online node” is, for example, a node that is assigned to continually deliver updates across the network and to always be online. However, offline nodes only need to download an updated copy of the ledger whenever they rejoin the network in order to remain in sync with all other nodes.
Types Of Crypto Nodes List
Let’s look at the crypto nodes list below to see the types of nodes in blockchain technology.
Light Nodes
Light nodes or “light nodes” do not store entire blockchain copies. Light nodes simply download block headers, saving consumers a substantial amount of download time and space. This kind of node relies on full nodes to operate and is used for streamlined payment verification (SPV).
Archival Full Nodes
When most people refer to a “full node,” they refer to a complete archived node. This is the fundamental sort of node that comprises the network’s backbone. Archival full nodes are servers that host the whole blockchain and record every transaction in their databases. These nodes are primarily responsible for validating blocks and maintaining consensus.
There are two kinds of archival nodes: those that can contribute blocks to the chain and those that cannot.
What are nodes in a crypto list?
Pruned Full Nodes
A pruned full node conserves storage space for its users by removing older blocks from the blockchain. First, this sort of node must download the complete blockchain from the beginning. Then, it will begin erasing blocks, starting with the oldest, until the node only stores the most recent transactions up to a predetermined size limit. If a node operator were to set the size restriction to 250 MB, a pruned complete node would have the 250 MB worth of most recent transactions.
Mining Nodes
In cryptocurrency mining, miners are either full or light nodes that attempt to demonstrate that they have performed the needed work to generate a new block. This is the origin of the phrase “proof-of-work.”
To do this duty, miners must either be archival full nodes themselves or get data from other nodes in order to determine the current state of the blockchain and how to proceed with locating the next block. Those seeking to operate mining nodes may want to consider cryptocurrency mining power expenses.
>> Recommend: How to mine Bitcoin at home, all the guides are here for you.
Authority Nodes
Consensus techniques for non-decentralized networks, such as Delegated Proof of Stake and Proof of Authority, use authority nodes. In these networks, either the development team or the community will choose how many authority nodes are required and who will operate them. These nodes provide the same function as complete nodes in other networks.

Types of node cryptos
Masternodes
Masternodes are incapable of adding blocks to a blockchain. They just verify and document transactions. Masternode operators may receive a portion of the network’s payouts. First, a fixed quantity of money must be locked away in the form of the network’s native token. DASH is an example of a master node-based network.
Lightning Nodes
Lightning nodes do not meet the profile of any previously described nodes. The primary purpose of a lightning node is to create a link between users outside the blockchain, hence facilitating “off-chain transactions”.
This minimizes network stress and enables significantly quicker and cheaper transactions. Lightning Bitcoin transactions generally cost between 10 and 20 satoshis, or a fraction of a cent.
Who Can Run A Crypto Node?
In conventional finance, payment networks such as Visa and PayPal are administered centrally. In the case of the vast majority of cryptocurrencies, the nodes of a blockchain do not need confirmation from the system’s top level since they check and verify each other using a consensus method.
Therefore, anybody around the globe may set up a node by installing the blockchain’s software onto their own computer.
However, not everybody can operate a masternode. Because the ability to operate a masternode might be exploited, the host is required to post a minimum (sometimes fairly significant) quantity of cryptocurrency as collateral. This collateral is held hostage if the masternode host breaches the blockchain’s regulations. The interest rate a masternode host gets is determined by multiplying their collateral deposit by the rate.

Who can operate node crypto?
Dash (DASH) is one of the most prevalent blockchains that have a masternode function. The minimum collateral required to qualify for running a masternode on the Dash blockchain is presently 1,000 DASH, valued at $200,000 at the time of publication. In 2016, for example, the DASH blockchain returned an annual interest rate of 11%, so it may still be a worthwhile investment.
At the time of writing, a website monitoring the live number of masternodes now operating on the DASH network reported that there are as many as 4450 masternodes in operation, with 1358 in Germany and 701 in the United States.
What Are Nodes Crypto’ Benefits When Operating A Node?
Primarily, running a node is crucial to ensure the efficient operation of a blockchain network. Nodes do not get money incentives, unlike miners. However, this does not negate the fact that the activity itself benefits both the person and the community.

What are nodes’ running advantages?
Running your own node raises the degree of security for your own transactions, first and foremost. This can supply you with much more independence. There is no need to employ a third-party provider. Obviously, this implies considerably more control over one’s finances than the traditional banking system.
In addition, you will contribute to the protection of the blockchain network’s security. Bitcoin would not exist without the efforts of these individuals!
In addition, you will be able to participate in the governance process. This means you have a genuine voice in matters such as system upgrades. And, in the case of a fork, you will be entitled to the same amount of cryptocurrency on the new network as your old balance.

Running a nodes crypto benefits
While you may need to increase your technical skills, you will be pleased to learn that operating a node is fairly inexpensive. Unlike other tasks, crypto mining does not require the use of costly supercomputers. The only prerequisites are a cheap computer, a reliable Internet connection, and a desire to understand certain technical elements.
The need for computational power is not limited to the issuance of new currencies. The network’s security level will increase according to the quantity of computational power. This prevents the network from being hacked. Maintaining Satoshi Nakamoto’s original concept for a genuinely decentralized network is also possible.
FAQs About Nodes Crypto
What Is The Function Of Nodes In A Blockchain?
The decentralized ledger known as the blockchain relies on people and their devices, which are represented by nodes, to verify activities.
How Many Nodes Exist On The Blockchain?
There are several varieties of blockchain nodes. The majority of them are variants of the archival full node that stores the complete ledger and provides governance privileges. However, light nodes, mining modes, masternodes, and lightning nodes also exist on the blockchain network and have their own purpose.
What Is A Bitcoin Node?
A network node helps verify Bitcoin blockchain transactions. Nodes receive and send data that facilitates the addition of new blocks and the creation of new Bitcoin.

What are nodes frequently asked questions
Are Crypto Wallet Nodes?
A wallet may be included in a full node that is used to verify transactions on the blockchain. Crypto wallets are not necessarily networked nodes since they do not automatically validate blockchain transactions. However, lightning nodes, which aid in the validation of off-chain transactions, may function as nodes. Moreover, complete nodes will provide a wallet function for users to keep their cryptocurrency.
>> What are crypto wallet definitions. Check out this post to explore.
Closing Thoughts
By using the Bitcoin P2P network protocol to connect with one another, Bitcoin nodes ensure the system’s security. The honest nodes rapidly identify a misbehaving node or one that attempts to spread false information and disconnect it from the network.
Running a fully validating node is strongly advised even though there are no financial benefits because it gives consumers a sense of trust, security, and privacy. The enforcement of the regulations is ensured by full nodes. They defend the blockchain from assaults and fraud (such as double-spending). A full node also removes the need for trust and gives the user complete control over his finances.

What Is A DApp – The Gateway To Interact Decentralized
22 March 2022