

Perpetual Swap Contract Working Mechanism With Perpetual Contract Example
06 June 2022
A perpetual swap contract or a perpetual futures contract also referred to as perpetual swaps for short, is a type of derivative trading product that has grown in popularity among crypto traders over the past few years. According to the available data, the average daily trading volume for perpetual swaps is over $180 billion.
Traders can use them to take large positions with relatively little capital, and they can generate substantial profits despite the fact that prices moved only slightly.
However, many people do not take the risks that are associated with perpetual swaps seriously, and as a result, they wind up losing their money, particularly when they use leverage. In order to make your journey through trading more secure and profitable, bePAY will explain in language that is accessible to beginners what perpetual swap contracts are and how you can incorporate them into your trading strategy.
What Is A Perpetual Swap Contract?
Cryptocurrency trading platform BitMEX first launched its perpetual swap trading product in 2016. Traders can make predictions about the future price movements of cryptocurrencies using a perpetual swap, which is similar to a forward contract in this respect.
Perpetual swaps differ from futures contracts in that they do not expire, unlike futures contracts. If you have a long or short position, this means you don’t have to keep setting it back up. These contracts must therefore be priced in accordance with the current market value of their assets. It is unnecessary to maintain a price peg. The value of the contract and the underlying asset automatically converge as the expiration date approaches.
A price anchoring system known as the funding rate mechanism is used by exchanges because perpetual swaps have no expiration dates. The short and long positions of perpetual swaps are balanced by either encouraging or discouraging trades through this mechanism. In a way, it’s a rebate or fee that helps to equalize the demand for perpetual contracts on the short and long sides.

What is a perpetual swap contract?
Here are some specific traits of a perpetual futures contract:
- There is no expiration date or settlement in this agreement.
- The price of perpetual contracts trades close to the underlying reference index price because they mimic a spot market based on margin.
- Contracts can be tethered to their underlying spot price using the funding mechanism.
- There are no significant differences between the prices of a futures contract and an underlying instrument.
Details about each contract can be found in the Contract Specifications section of the contract. These are the specifics:
- Reference Index
- Funding Rate
- Maximum Leverage
How Does The Perpetual Swap Contract Work?
To clarify how the perpetual swap contract works, let’s take this perpetual contract example.
The Market Happens As If According To Plan
By providing $60,000 in collateral, Alice purchases 2 BTC/USD perpetual swaps. Consequently, each BTC/USD perpetual swap is valued at $30,000. Assuming the price of bitcoin steadily increases to $40,000 the following month and Alice decides to close her position, she would have made a profit of $10,000 on each perpetual swap she purchased. Her total earnings would be approximately $20,000.
Perpetual profit equals the number of perpetual swaps * (current price – entry price)
- Profit = 2 * ($40,000 – $30,000)
- Profit = $20,000
It is important to note that this calculation does not account for the impact of funding rates on Alice’s profitability. The exact number that Alice generates would be determined by the fees. She pays the rebate she receives as a result of the exchange’s attempt to peg the perpetual swap to the bitcoin spot price.
Perpetual contract examples
Additionally, Alice could multiply her profits by utilizing the leverage opportunities available to traders of perpetual swaps. To accomplish this, she could purchase perpetual contracts worth twice the initial collateral deposit. Using this strategy, the size of her position would be $120,000 (or 4 BTC/USD perpetual swaps), despite the fact that her collateral represents only 50% of the value of the perpetual swaps she trades.
In this scenario, Alice has utilized twofold leverage. If she closes her position when each BTC/USD perpetual swap sells for $40,000, she will realize a profit of approximately $40,000.
- Profit = 4 * ($40,000 – $30,000)
- Profit = $40,000
However, What Happens When The Market Goes Another Way?
Intriguingly, certain exchanges permit traders to utilize up to 125x leverage to maximize profits. However, in the same way that leverage magnifies profits, it also magnifies losses. Alice is exposed to liquidation risk if the price of the perpetual swaps falls by 50% from the initial price at which she purchased them if she uses 2x leverage.
- Profit = 4 * ($20,000 – $30,000)
- Loss = $40,000
When a trader’s unrealized loss equals the collateral deposited, the exchange closes the trader’s position automatically. Consequently, the entire collateral would be lost. Therefore, the risk associated with using margins or trading with leverage is substantial, and novice traders should NOT engage in such practices.

Perpetual swap contracts are extremely risky
>> Recommend: Maximizing your opportunities with arbitrage trading crypto
What Is The Funding Rate And Its Effect On The Perpetual Contract?
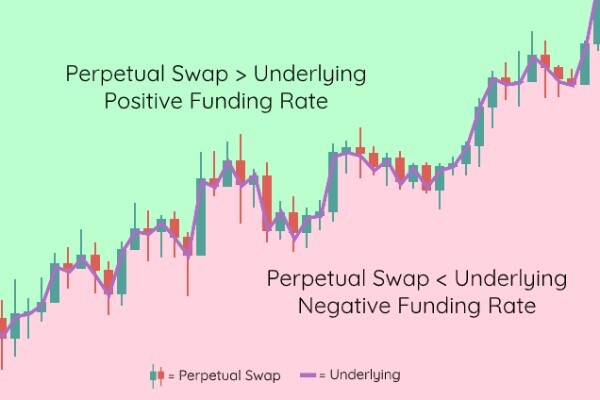
Using funding rates, perpetual swaps track the spot price of the underlying asset. The perpetual swap price, the underlying price, and the funding rate are shown in the following diagram:
The main difference between the two possibilities is shown above. When the price of a perpetual swap trades higher than the price of the underlying (in the green area), the funding rate is positive. The perpetual swap price will fall in line with the underlying asset if long traders pay short traders. This will discourage buyers and encourage sellers.
The funding rate is negative when the price of the perpetual swap is lower than the price of the underlying (see the red area in the chart above). Short traders will pay long traders, which discourages selling and encourages buying, resulting in a rise in the perpetual swap price that matches the value of the underlying asset.
Funding rates affect
In a follow-up post, we’ll examine the specifics of how each exchange calculates funding rates and processes payments. As a general guideline, funding rates typically range from -0.025% to 0.025%. A normal funding period is 8 hours.
A trader with a $100,000 Bitcoin perpetual swap position would either pay or receive a $25 funding fee. As a starting point, remember that a perpetual swap maintains equilibrium by paying a rate of interest to satisfy both supply and demand. The interest rate needed to bring the perp’s price back into line is minimal if the perp’s price is close to the spot. The interest rate rises in direct proportion to the distance from the goal.
What Is The Difference Between Perpetual And Inverse Perpetual?
When compared, what is the difference between perpetual and inverse perpetual? A perpetual contract is a linear contract. The USDT, or other stablecoin, is the margin used for linear contracts. On the other hand, in an inverse perpetual contract, a trader who wishes to trade a BTC/ETH/XRP/EOS contract must use the underlying cryptocurrency as a margin in order to trade the inverse perpetual contract.
The USDT perpetual contract includes the following:
The margin and profit and loss calculations for USDT perpetual contracts are more straightforward than those for inverse perpetual contracts. When trading 1 BTC and the price changes by 100 USDT, the trader will make or lose 100 USDT. The profit and loss graph for USDT contracts will be linear.

Perpetual and inverse perpetual
Meanwhile, the inverse perpetual contract is traded based on the cryptocurrency underlying it. As a margin, traders must hold the much more volatile BTC/ETH/EOS/XRP.
Consequently, even if traders choose not to trade, holding a cryptocurrency carries inherent risks. The USDT perpetual contract, on the other hand, uses stablecoin as a margin, so traders do not need to hedge their position to avoid the risk associated with holding the cryptocurrency.
| Compared Traits | Perpetual contracts | Inverse perpetual contract |
| Base Currency | Use USDT or other Stablecoins | Use the underlying cryptocurrency as a base currency. |
| Margin, PNL | Calculated by USDT or stablecoin of trading pair (e.g., BTC/USDT, BTC/BUSD) | Calculated by base currency like BTC/ETH/EOS/XRP |
| Risk | Less risk rather than an inverse perpetual contract, which causes the stability of stablecoin | Much more dangerous when holding the assets due to margin and volatility of base currency (BTC/ETH/XRP) |
>> Recommend: How to survive through the bear market with tips
FAQs About Perpetual Swap Contracts
Do You Have A Trading Platform For Perpetual Swaps?
Derivatives exchanges such as OKEx, ByBit, and BitMEX offer perpetual swaps for trading. Customers who have purchased spots via this channel can now trade them on popular crypto exchanges like Binance and Coinbase. As a result, exchanges that had previously only offered derivatives are increasingly venturing into the spot market as a result.
Should You Invest In Perpetual Swaps?
For experienced traders, perpetual swaps provide multiple benefits, including the ability to use leverage and hedge positions, as well as a number of other advantages.
However, these financial instruments carry a high level of risk. The cryptocurrency markets are notoriously unstable, and the use of leverage tends to make the situation even worse. Before you start trading, you should ask yourself if you can withstand the financial blow of losing your entire initial deposit.
Perpetual Swaps Vs Spot Crypto: Which Should I Choose?
Profiting from a rise in the value of cryptocurrency can be done by purchasing and holding “spot” cryptocurrency. A traditional “buy low, sell high” scenario is at play here. However, all markets can be profited from by experienced traders. If the price of a perpetual swap drops, the trader who opened a short position stands to profit.

Spots or perpetual swap
Closing Thoughts
Perpetual swaps represent the right to purchase or sell an underlying asset at any time in the future. Perpetual swaps are a powerful tool for traders who wish to profit from the price fluctuations of an asset without actually holding the asset.
However, not possessing the underlying asset, however, eliminates the possibility of staking or lending it. In addition, Leveraged trading necessitates careful consideration of the desired level of risk exposure. The availability of high leverage ultimately made perpetual swaps the most actively traded cryptocurrency instrument by volume.
Currently, centralized exchanges dominate the perpetual swap market. Compared to centralized solutions, decentralized perpetual swap platforms account for less than one percent of the market share. Ultimately, decentralized exchanges provide traders with a superior value proposition.
The majority of decentralized exchanges distribute their revenue to their users, such as the liquidity providers on Uniswap. Common DeFi revenue distribution models allow users to directly profit from the exchange’s long-term adoption.

Detailed Guide Of How To Add Arbitrum To Metamask
15 July 2022
What Is BSCScan? Ultimate Guides For Newbies
29 March 2022
Exploring How To Create A Metamask Wallet And Its Usages
10 March 2022
Step By Step Guide Of How To Add Polygon To MetaMask
16 June 2022






