Lightning Network – The Vital Mission To Bring Bitcoin To Everyone
28 April 2022
Cryptocurrencies possess several distinctive characteristics. They cannot be readily hacked or shut down, and anybody may use them to move value around the world without the involvement of a third party.
To maintain these characteristics, considerable trade-offs must be made. Because a cryptocurrency network is maintained by a large number of nodes, throughput is constrained. As a consequence, the number of TPS that a blockchain network can handle is rather low for a system aimed at widespread adoption.
To address the inherent constraints of blockchain technology, many scaling methods have been suggested to expand the number of transactions that a network can process. bePAY’ll take you to a deep dive into what is Lightning Network, one such extension of the Bitcoin protocol, in this post.
- What Is Lightning Network?
- How Does Lightning Network Work?
- The Lightning Network Pros And Cons?
- Real-World Applications Of The Lightning Network
- FAQs About Lightning Network
- Closing Thoughts
What Is Lightning Network
Lightning Network Explained
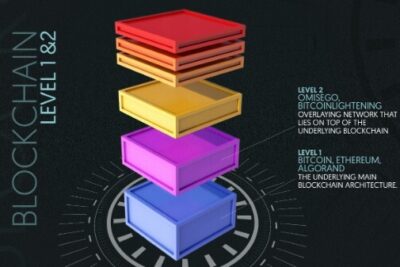
The Lightning Network (abbreviated as LN) is a scaling solution built on top of Bitcoin that enables users to send and receive Bitcoin rapidly and with nearly no costs.
Lightning is a Layer 2 solution that operates off-chain, which means that payments are made through a new network of payment channels rooted in Bitcoin’s blockchain.
As the world’s first and most widely used cryptocurrency, Bitcoin has established itself as a significant medium of exchange since, for the first time, every holder can:
- Maintain bitcoin in the absence of unforeseen supply inflation
- Without the need for an intermediary, send and receive bitcoin.
- Validate transactions by the use of their nodes

Lightning Network Explained
However, many think that Bitcoin requires further functionality to achieve its initial goal of becoming a worldwide medium of exchange and peer-to-peer electronic currency system, as outlined in the foundational whitepaper Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. Bitcoin now faces the following limitations:
- Fees — Due to the restricted amount of block space available, mining fees might change significantly depending on the demand for transaction inclusion.
- Transactions per second — Bitcoin has a maximum transaction rate of roughly seven per second
- Congestion on the network – Slow block timings and increased network use might result in delays in transaction confirmations.
The Bitcoin Lightning Network promises to address these restrictions by enabling rapid and affordable transactions at a rate of about 1 million per second.
While Lightning may be used for any sort of transfer, the majority of users find it handy for micropayments and other tiny transactions that are generally uneconomical owing to base layer costs.
It’s critical to understand that the Lightning Network does not introduce a new currency and maintains the same liberties as Bitcoin – it’s decentralized, permissionless, and open source. Its security stems from on-chain Bitcoin transactions, which make use of smart contracts to provide rapid, off-chain settlements.
>> Read Also: What Is Behind Smart Contract Technology – Smart Contract Examples
Key Elements Of Lightning Network
- The Lightning Network allows users to conduct bitcoin transactions in a near-instantaneous manner.
- The Lightning Network demonstrates how Bitcoin might become a worldwide medium of trade without jeopardizing the network’s security or decentralization.
- While the Lightning Network is operational, it is still experimental and should not be utilized for large-volume storage or transactions.

Bitcoin Lightning Network
Numerous Implementations of Lightning
Wallets use a variety of Lightning Network node implementations. Lightning Labs’ Lightning Network Daemon, ACINQ’s Eclair, and Blockstream’s c-lightning are all popular examples.
While each of these three implementations is implemented in a distinct programming language, they are all interoperable. All Lightning implementations adhere to the BOLT standards, a set of criteria that ensures Lightning implementations achieve consensus and compatibility. There is just one Lightning Network protocol, as defined by the BOLT standards.
How Does Lightning Network Work?
The Lightning Network establishes off-chain payment channels between pairs of users via the use of smart contracts. After establishing these payment channels, monies may be exchanged very instantaneously between them.
The network can avoid creating couples between all users by being clever. In this case, when User A shares a channel with User B and User C shares a channel with User B but not with User A, cash may still be exchanged freely between all networked participants. Lightning addresses resemble conventional Bitcoin addresses, and the user experience is quite similar.
Users may terminate payment channels and settle their final balances on the main blockchain at any moment.
Due to the fact that the core blockchain records simply the opening and closure of payment channels, the whole Bitcoin network may operate more quickly. Even more so, transactions on the Lightning Network are more secure than those on the Bitcoin blockchain (because layer 1 transactions all appear on a public and transparent ledger).

How Does Lightning Network Work?
The Lightning Network Pros And Cons?
Pros Of The Lightning Network
Quicker and Cheaper
The apparent benefits of the Lightning Network are quicker and cheaper transactions, which enable micropayments in previously unimaginable ways. Without the Lightning Network, customers would have to pay hefty transaction fees and then wait an hour or more for the transaction to process.
Smaller transactions have longer wait times because miners prefer to validate bigger transactions since they gain a higher reward for doing so.
Security
The Lightning Network is an additional layer built on top of the Bitcoin network. As a result of the link, the Lightning Network continues to benefit from Bitcoin’s security standards. Users may then safely use the main blockchain for larger transactions and the Lightning Network’s off-chain for smaller ones.
Additionally, the Lightning Network payment channels allow secret transactions, since observers cannot see individual transactions but only the package as a whole.
Without Middlemen
Additionally, cryptocurrency fans have been experimenting with atomic swaps, which is the act of exchanging one cryptocurrency for another without the assistance of a third party or an exchange. Atomic Swaps are more advantageous than exchanges since they enable near-instant exchanging with little to no costs or wallet transfers.
Reduced energy consumption
Allow us to acknowledge that the story around Bitcoin’s energy usage has been detrimental to the cause – but the Lightning Network rectifies this. It grows non-linearly with energy use and is meant to operate on a peer-to-peer network, exploiting existing connections.
In essence, as the second layer, it facilitates off-chain transactions by avoiding the computational strain associated with confirming blocks on-chain or uploading transactions to the blockchain.

Lightning Network Benefit
Cons Of The Lightning Network
Hard To Use If You’re Not A Techie
To use the Lightning Network, one must first buy a wallet that is compatible with it. While locating a wallet that supports the Lightning Network is straightforward, the wallet must be funded using a standard Bitcoin wallet. Because the first transaction between the standard and Lightning Network wallets incurs a charge, users forfeit some Bitcoin in order to communicate with the protocol.
After depositing money into their Lightning Network wallets, users must secure their Bitcoin in order to establish a payment channel.
Transferring Bitcoin between wallets may be inconvenient and costly, which may turn new users off. Nonetheless, some wallets support both on- and off-chain payments without incurring fees, and convenience is expected to increase with time.
>> Read Also: What Is Crypto Wallet? And Why It’s Necessary For All Crypto Users
Small Users Maybe Harmful
If any payment channel member wants to withdraw money, they must actively shut the channel and reclaim the Bitcoin before spending the funds. It is not feasible, for example, to withdraw a little amount of money while leaving the channel open.
Even stopping or creating a payment channel needs an initial transaction known as a routing cost. While the premise of starting a channel is straightforward, all of these additional fees make the procedure more costly than many prospective customers are willing to pay.
Users May Be Scammed
However, one of the most serious issues with the Lightning Network is offline transaction fraud. If one party to a payment channel decides to end it while the other party is offline, the former party has the opportunity to steal the cash. When the latter party eventually comes online, there is nothing that can be done. The fraudster might just disappear, leaving no method to reach them.
Additionally, the Lightning Network has issues, such as blocked payments, which are unverified outbound transactions. The Bitcoin network will reimburse a stopped payment, although it may take days to process since genuine transactions have higher priority for verification than stuck transactions.

Lightning Network Drawbacks
>> Read Also: What Are Shapes Of Cryptocurrency Scams – Tips To Avoid Crypto Scams
Regulation Issues
Finally, even if the Lightning Network resolves all of its flaws, regulators remain a concern. Regulators may struggle to have a sufficient understanding of the Lightning Network in order to adopt appropriate regulations. If regulators encounter difficulties, mainstream cryptocurrency consumers may have similar difficulties when attempting to utilize the Lightning Network.
Even if authorities comprehend the protocol, the Lightning Network’s secrecy may prevent them from approving it. Legislators may be put off by anonymous transactions since they can only see a finished transaction once a user shuts their payment channel, not the individual transactions inside the channel.
Real-World Applications Of The Lightning Network
Through the Lightning Network, Twitter users may give and receive Bitcoin “tips.” Many of Twitter’s 360 million monthly active users may now transfer Bitcoin payments to other Twitter accounts immediately and for free using Strike, a Lightning Network-compatible payments software. (Twitter is not the first creator-driven social site to integrate the Lightning Network; Substack has been accepting Bitcoin payments since late August.)
El Salvador became the first country to legalize Bitcoin – in part to save Salvadorans over $400 million in yearly money transfer costs. Chivo, a wallet produced by the government, is Lightning-compatible and is intended to facilitate smooth cross-border payments. Chivo was routinely one of the top downloaded applications in El Salvador as of October.
Paxful, a peer-to-peer Bitcoin exchange that conducts millions of dollars worth of Bitcoin transactions in underdeveloped areas and boasts 1.5 million users in Africa alone, also revealed later that it would accept Lightning payments. This connection might allow millions of consumers to make quick and inexpensive Bitcoin payments.

Lightning Network Usecases
>> Read Also: Exploring Peer-To-Peer NetWork, Maximize Your Opportunity With P2P Trading
FAQs About Lightning Network
What Is The Definition Of A Lightning Payment Channel?
A Lightning channel is a two-way payment channel, which means that both parties may send and receive money via it. The Lightning Network is comprised of Lightning channels, each of which has a set bitcoin capacity. This capacity is shared by the channel’s two parties, and bitcoin is transferred between them through Lightning transactions.
Who Is Responsible For The Lightning Network’s Development?
Thaddeus Dryja and Joseph Poon announced the Lightning Network in 2015 in their white paper, ‘The Bitcoin Lightning Network: Scalable Off-Chain Instant Payments.’
How Can You Begin Using The Lightning Network?
To use the Lightning Network, you must first transmit some BTC (from your Coinbase account, for example) to a Lightning-compatible wallet. There are many of options. Wallets classified as “custodial” or “non-custodial” are popular. The distinction is as follows:
Wallets in custody: Strike, Blue Wallet, and Satoshi’s Wallet are all options. These are often recommended for novices since they ease the process of sending and receiving cryptographic messages by maintaining your private keys. If, for example, you forget your password, you may reset it.

Lightning Network FAQs
Muun, Breez, Phoenix, and Zap are all examples of non-custodial wallets. These are user-controlled wallets that are popular among more experienced traders — nobody but you has access to your private keys. If you misplace, damage, or forget your wallet’s password, you risk losing access to your assets. Therefore, ensure that you understand how to backup and restore any wallet you use.
Closing Thoughts
The Bitcoin Lightning Network is still vulnerable to fraud and malicious attacks due to the lack of security mechanisms in place on card networks. If someone hijacked your account and used your money to purchase products and services through the Network, you would be unable to recover them.
You must safeguard your credentials, educate yourself, and assume personal responsibility for your safety. This is often seen as a barrier for small enterprises and startups with their fingers in several pies.
Combining the Lightning Network with Bluetooth technology enables offline confirmation and facilitation of transactions without the requirement for a TCP/IP connection to the internet. If you ever find yourself in a nation where particular platforms or technologies on certain servers, such as the Lightning Network, are unavailable, you will need an offline consensus.
The Lightning Network is capable of processing possibly infinite transactions per second cheaply and effectively while preventing the blockchain from being overburdened. It is still relatively new, yet it is critical to the future success of crypto payments.

What Are Stablecoins And Why Do You Need Them?
10 March 2022
What Is A DApp – The Gateway To Interact Decentralized
22 March 2022