

What Is Avalanche Network? Is It An “Ethereum Killer” As Gossip?
31 May 2022
If you are seeking a blockchain that has the same features as Ethereum but has a cheaper cost, higher transaction confirmation rates, and quicker speeds. It would seem that the Avalanche network is one of the most qualified contenders for this role. There is no room for overestimation when it is given the label “Ethereum Killer,” so why is it given that name?
If you are looking for information on the Avalanche network, you have come to the correct spot since bePAY has all the details you need. In this post, you will discover information that is helpful about Avalanche networks. We will take a tour through the in-depth information on Avalanche networks, including a definition of what exactly an Avalanche network is. In what ways does it operate? as well as native AVAX tokenomics.
What Is Avalanche Network?
The Avalanche network is a framework for the development of unique blockchain networks and decentralized apps (dApps). The Avalanche crypto platform was made by Ava Labs. It is one of several projects that are trying to replace Ethereum as the most widely used smart contract platform in the blockchain ecosystem.

What is Avalanche network?
Avalanche asserts that it has a high transaction throughput of 4,500 TPS. Avalanche has attempted to compete with Ethereum by establishing its own decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem, and bZx, SushiSwap, Reef, Securitize, and TrueUSD are just some of the Ethereum-based DeFi apps that have integrated with its platform. Avalanche is also building a bridge to the Ethereum network, which will make it easy for users to move assets between the two chains.
Avax Tokenomics
- Ticket: $AVAX
- Max Supply: 720 million
- Total Supply: 404 million
- Circulation Supply: 220 million
- Locked Supply: 171 million

Avax tokenomics
AVAX is Avalanche’s native token, and its maximum capped supply is 720 million. As a deflationary mechanism, all network fees are burnt, which benefits the Avalanche community as a whole. AVAX has three primary uses:
- You may stake your AVAX in order to become a validator or delegate it to a validator. Validators may earn up to 10% Annual Percentage Yield (APY) and establish a bespoke percentage charge of the reward they retain from delegators that support them.
- AVAX is the universal unit of account for all subnets, enhancing interoperability.
- Subnet subscriptions and transaction costs are charged in AVAX.
- The burning of AVAX transaction fees increases the scarcity of AVAX.
Token Distribution
The Avax token distribution is as follows
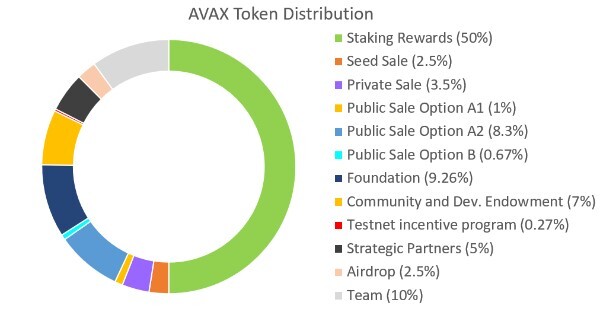
Avax token distribution
How Does Avalanche Work?
Even though Avalanche’s platform is complicated, it is different from other blockchain projects because it uses a consensus method, has subnetworks, and has many blockchains built in.
Avalanche Consensus
A blockchain network needs a protocol that lets its nodes come to an agreement so that transactions can be checked and network security can be kept up. Regarding cryptocurrencies, the discussion has concentrated on Proof of Work (PoW) vs Proof of Stake (PoS) as the dominant approaches for achieving consensus.
Avalanche employs a revolutionary consensus process that is based on PoS. When a user starts a transaction, it is accepted by a validator node, which picks a small group of other validators at random to check if they agree. The validators do this sampling process several times and “talk” with each other until they come to an agreement.
In this way, the message from one validator is sent to other validators, which then sample more validators, and so on, until the whole system agrees on a conclusion. Similar to how a single snowflake may grow into a snowball, a single transaction can grow into an avalanche.
Proof of Uptime is how long a node has been staking its tokens, and Proof of Correctness is whether or not the node has always followed the rules of the software.
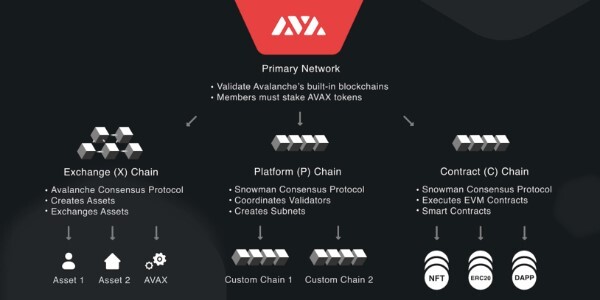
How does Avalanche work?
Subnetworks
Avalanche users are able to initiate customized chains with their own sets of rules. This scaling method for blockchains is similar to Polkadot’s parachains and Ethereum 2.0’s shards, which were used in the past.
Subnetworks (or subnets) are groupings of nodes that engage in verifying a certain set of blockchains and obtaining consensus on these chains. All subnet validators must also verify the primary network of the Avalanche.
Integrated Blockchains
Avalanche is built with three different blockchains to get around the blockchain trilemma. Digital assets can move through each of these chains to help the environment in many ways.
- The Exchange Chain (X-Chain) is the default blockchain for creating and exchanging assets. This contains the native Avalanche token, AVAX.
- The Contract Chain (C-Chain) enables the development and execution of smart contracts. Avalanche’s smart contracts may take advantage of cross-chain interoperability due to their reliance on the Ethereum Virtual Machine.
- The Platform Chain (P-Chain) facilitates the development and maintenance of subnets and coordinates validators.
Avalanche Vs Solana In
The Similarities
There are a number of characteristics that make them both similar and distinct. Such as having a limited supply. We are all used to seeing endless currency today, but both of them have a finite number of tokens that will ever be issued.
They are both open-source projects, whose source code is accessible. This gives them greater trust since people can verify the code to determine whether it contains malicious code (which it does not).
Lastly, they are both “ETH Killer” projects, meaning that their whole marketing strategy is centered on being superior to ETH. This indicates that they want it to be scalable to the point where it could be used by millions of people every day and yet carry the same load.

Avalanche vs Solana
The Differences
The distinctions are less about why one is superior to the other and more about how each approaches the same problem. Avax, for instance, uses three distinct blockchains to address the same issue that Solana solves with a single Blockchain.
While Avax might function over three distinct networks, SOL only operates on a single network. While SOL is capable of up to 65,000 transactions per second, Avax is far lower. Overall, they both tackle the ETH gas fee issue, albeit they do so in different ways.
Avalanche vs Solana quick looks:
| Evaluated traits | Avalanche | Solana |
| Network Validators | 2200 | 20 |
| Block Time | 0.8 seconds | 0.4 seconds |
| Consensus Mechanism | Proof of Stake (POS) | Proof of Stake (POS) |
| EVM Compatible | Yes | No |
| Secure Bridging | Yes | Yes |
| Transaction Fees | $0.01 | $0.0001 |
>> You are a deep learner, here is all you need to know about Solana Network
FAQs About Avalanche
Is Avalanche Safe?
Although the Avalanche network lacks block leaders, it is robust enough to withstand huge network assaults. A hacker must simultaneously possess 80% of validators in order to attack Avalanche.
To attack Bitcoin’s network, on the other hand, you need to have 51% of its processing power. For the majority of Proof of Stake blockchains, between 50 and 66% of the total coins in circulation are required to break the protocol.
This makes Avalanche much more secure than any other blockchain network currently in existence.
>> Related: Interested in a 51% attack
Is Avalanche Crypto A Good Investment?
It is possible. The price expectations are rather optimistic. However, we must emphasize that projections may be and often are incorrect, so you should always do your own research before investing.

Is Avalanche crypto a good investment?
What Are The Potential Risks Of Avalanche?
Even though Avalanche has no obvious flaws, it is still a young business in a very competitive field. Numerous prominent smart contract blockchains started development years before Avalanche, giving them more opportunities to establish themselves. Moreover, there are always new initiatives seeking to surpass industry leaders, just as Avalanche did throughout its ascent.
Also contested is whether or not the Avalanche network is genuinely decentralized. The project is managed by Ava Labs, which has considerable influence. In all fairness, the majority of businesses behind the big blockchain projects play a significant part in their functioning, so Avalanche is not unique in this respect.
Closing Thoughts
With decentralized finance firms seeking Ethereum alternatives, EVM compatibility, and cheap costs make blockchains like Avalanche appealing. But when it comes to scalability and performance, DeFi systems already have a large number of options.
Avalanche has gained in popularity since its debut and has already surpassed Ethereum in terms of daily transactions, but it remains to be seen if it can compete with other blockchains like Solana or Polygon.

What Is Tendermint? What Makes Tendermint Great?
30 July 2022










